Disruptor是英国外汇交易公司LMAX开发的一个高性能队列,研发的初衷是解决内存队列的延迟问题(在性能测试中发现竟然与I/O操作处于同样的数量级)。基于Disruptor开发的系统单线程能支撑每秒600万订单,2010年在QCon演讲后,获得了业界关注。2011年,企业应用软件专家Martin Fowler专门撰写长文介绍。同年它还获得了Oracle官方的Duke大奖。
正在使用的disruptor的开源软件
- Apache Storm
- Camel
- Log4j 2
源码下载
git clone https://github.com/LMAX-Exchange/disruptor
本文使用的版本是3.4.2
创建一个disruptor
/**
* Create a new Disruptor.
*
* @param eventFactory the factory to create events in the ring buffer.
* @param ringBufferSize the size of the ring buffer, must be power of 2.
* @param threadFactory a {@link ThreadFactory} to create threads for processors.
* @param producerType the claim strategy to use for the ring buffer.
* @param waitStrategy the wait strategy to use for the ring buffer.
*/
public Disruptor(
final EventFactory<T> eventFactory,
final int ringBufferSize,
final ThreadFactory threadFactory,
final ProducerType producerType,
final WaitStrategy waitStrategy)
{
this(
RingBuffer.create(producerType, eventFactory, ringBufferSize, waitStrategy),
new BasicExecutor(threadFactory));
}
producerType对应具体的生产者模式。
/**
* Defines producer types to support creation of RingBuffer with correct sequencer and publisher.
*/
public enum ProducerType
{
/**
* Create a RingBuffer with a single event publisher to the RingBuffer
*/
SINGLE,
/**
* Create a RingBuffer supporting multiple event publishers to the one RingBuffer
*/
MULTI
}
使用哪个模式取决你的生产者到底是单线程还是多线程。多线程的模式在预分配的过程中会使用CAS来保证数据的一致性(同一个槽不会被不同的生产者占用)
WaitStrategy–消费者等待策略。一旦消费者的处理速度比生产者快,消费者所采用的等待策略
| 等待策略 | 措施 | 适用场景 |
|---|---|---|
| BlockingWaitStrategy | 加锁 | CPU资源紧缺,吞吐量和延迟并不重要的场景 |
| BusySpinWaitStrategy | 自旋 | 通过不断重试,减少切换线程导致的系统调用,而降低延迟。推荐在线程绑定到固定的CPU的场景下使用 |
| PhasedBackoffWaitStrategy | 自旋 + yield + 自定义策略 | CPU资源紧缺,吞吐量和延迟并不重要的场景 |
| SleepingWaitStrategy | 自旋 + yield + sleep | 性能和CPU资源之间有很好的折中。延迟不均匀 |
| TimeoutBlockingWaitStrategy | 加锁,有超时限制 | CPU资源紧缺,吞吐量和延迟并不重要的场景 |
| YieldingWaitStrategy | 自旋 + yield + 自旋 | 性能和CPU资源之间有很好的折中。延迟比较均匀 |
具体的等待策略的源码暂时不在这里做分析
创建RingBuffter,disruptor适用的一个环状缓冲结构。RingBuffer有一个很核心的组件sequencer。多生产者模式和单生产者模式的主要区别就是在这里。我们先在脑海里记得有这么个组件,它的主要作用后面再进行分析。
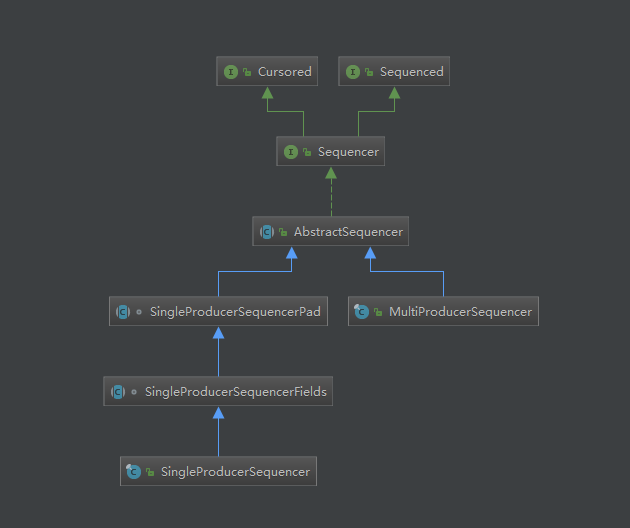
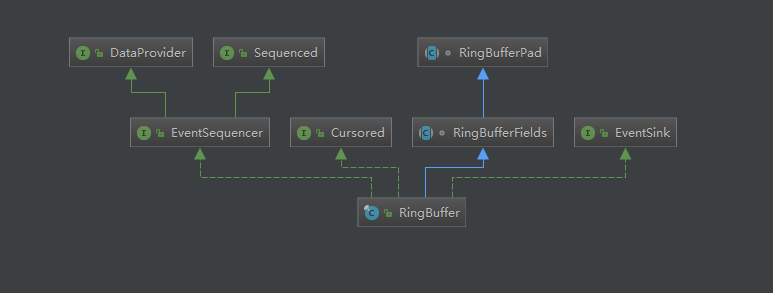
生产者
我们先关注最简单的单生产者的模式。下面的方法是最常用的,把参数arg0转化成泛型E,然后写入到队列。
RingBuffer.java
/**
* @see com.lmax.disruptor.EventSink#publishEvent(com.lmax.disruptor.EventTranslatorOneArg, Object)
* com.lmax.disruptor.EventSink#publishEvent(com.lmax.disruptor.EventTranslatorOneArg, A)
*/
@Override
public <A> void publishEvent(EventTranslatorOneArg<E, A> translator, A arg0)
{
final long sequence = sequencer.next();
translateAndPublish(translator, sequence, arg0);
}
调用关系图
graph LR
Disruptor-->RingBuffer
RingBuffer-->sequencer
RingBuffer--entries-空间预分配-->RingBuffer
sequencer-->next-获取队列的序号
sequencer-->publish-更新队列头尾指针
何如获取RingBuffer下一个槽的序号?
/**
* @see Sequencer#next(int)
*/
@Override
public long next(int n)
{
if (n < 1)
{
throw new IllegalArgumentException("n must be > 0");
}
long nextValue = this.nextValue;
long nextSequence = nextValue + n;
long wrapPoint = nextSequence - bufferSize;
long cachedGatingSequence = this.cachedValue;
if (wrapPoint > cachedGatingSequence || cachedGatingSequence > nextValue)
{
cursor.setVolatile(nextValue); // StoreLoad fence
long minSequence;
while (wrapPoint > (minSequence = Util.getMinimumSequence(gatingSequences, nextValue)))
{
LockSupport.parkNanos(1L); // TODO: Use waitStrategy to spin?
}
this.cachedValue = minSequence;
}
this.nextValue = nextSequence;
return nextSequence;
}
对于单生产者来说,只需要针对nextValue进行自增。注意单生产者没有对nextValue进行加锁,如果是多生产者的模式则需要对nextValue用CAS的方式保证nextValue的线程安全。
我们增加一个单元测试来关注sequencer的属性变化。
@Test
public void next(){
SingleProducerSequencer sequencer = new SingleProducerSequencer(16, new BusySpinWaitStrategy());
for (int i = 0; i < 32; i++){
long next = sequencer.next();
sequencer.publish(next);
System.out.println("cursor:"+sequencer.cursor);
System.out.println("nextValue:"+sequencer.nextValue);
System.out.println("wrapPoint:"+(sequencer.nextValue-sequencer.bufferSize));
System.out.println("cachedValue:"+sequencer.cachedValue);
String values="";
for(Sequence sequence:sequencer.gatingSequences){
values+=sequence.get()+",";
}
System.out.println("gatingSequences:"+values);
System.out.println();
}
}
cursor:0
nextValue:0
wrapPoint:-16
cachedValue:-1
gatingSequences:
cursor:1
nextValue:1
wrapPoint:-15
cachedValue:-1
gatingSequences:
...
cursor:15
nextValue:15
wrapPoint:-1
cachedValue:-1
gatingSequences:
cursor:16
nextValue:16
wrapPoint:0
cachedValue:15
gatingSequences:
...
cursor:31
nextValue:31
wrapPoint:15
cachedValue:15
gatingSequences:
Process finished with exit code 0
wrapPoint相当于RingBuffer的头指针
cursor相当于RingBuffer的尾指针
消费者
BatchEventProcessor是EventProcessor的子类。
private void processEvents()
{
T event = null;
long nextSequence = sequence.get() + 1L;
while (true)
{
try
{
//这里涉及到消费者的等待策略的逻辑
final long availableSequence = sequenceBarrier.waitFor(nextSequence);
if (batchStartAware != null)
{
batchStartAware.onBatchStart(availableSequence - nextSequence + 1);
}
while (nextSequence <= availableSequence)
{
event = dataProvider.get(nextSequence);
//消费者事件执行的逻辑
eventHandler.onEvent(event, nextSequence, nextSequence == availableSequence);
nextSequence++;
}
sequence.set(availableSequence);
}
...
}
}
问题
- disruptor为什么快?
- SequenceBarrier的作用?
- disruptor的handleEventsWithWorkerPool和handleEventsWith的区别?
参考文献
dissecting-disruptor-wiring-up
重点关注 How consumer dependencies work in the Disruptor
如何使用Disruptor(二)如何从Ringbuffer读取
比较重要,介绍RingBuffer的数据读取流程。
