一、seata是什么
Seata 是一款开源的分布式事务解决方案,致力于提供高性能和简单易用的分布式事务服务。Seata 将为用户提供了 AT、TCC、SAGA 和 XA 事务模式,为用户打造一站式的分布式解决方案。
在19年初的时候就关注过这个中间件(当时叫Fescar),并且对它的源码进行了一下分析–阿里分布式事务解决方案fescar简析。然而当时并不成熟,并不能直接用于商用,主要有以下几个问题。
- TC的实现不完善。不支持HA,xid的生成,session的存储,锁的实现等都是以DEMO的方式提供,不能直接用于线上环境,需要二次开发
- 回滚失败的补偿机制不完善
- 性能问题。seata当时宣称只有在第一阶段提交的时候进行加锁,相对传统的两阶段提交对性能有比较大的提升。但现实情况是为了保证回滚操作的成功,还必须要有一个全局锁,事实上相比XA的方式我个人认为在系统的吞吐量上个人认为不会有太大的变化。而且由于这种方式实现的是类似补偿性事务的方式,又会引入一个可见性的问题(第二阶段提交前就已经能看到第一阶段提交的结果)
- RPC框架。由于是阿里系的中间件,因此第一版实现的是基于dubbo,非dubbo的rpc框架需要根据自己的情况做二次开发。(新版本已支持euraka、nacos等服务注册中心)
二、理论基础
- cap原则
- base理论
三、分布式事务的解决方案
- 2PC(XA、AT?)
- 补偿型事务(TCC、SAGA)
- 可靠消息(rocketmq,消息表)
- 最大努力通知
| 类型 | 2PC | TCC(补偿型事务) | SAGA(补偿型事务) | 可靠消息 | 最大努力通知 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 一致性 | 强一致性 | 最终一致性 | 最终一致性 | 最终一致性 | 最终一致性 |
| 吞吐量 | 低 | 中 | 中 | 高 | 高 |
| 实现复杂度 | 低 | 高 | 中 | 中 | 中 |
四、模式
- AT
- TCC
- SAGA(新特性)
类似一个业务总线的方式把各个分布式资源串联起来?

- XA(新特性)
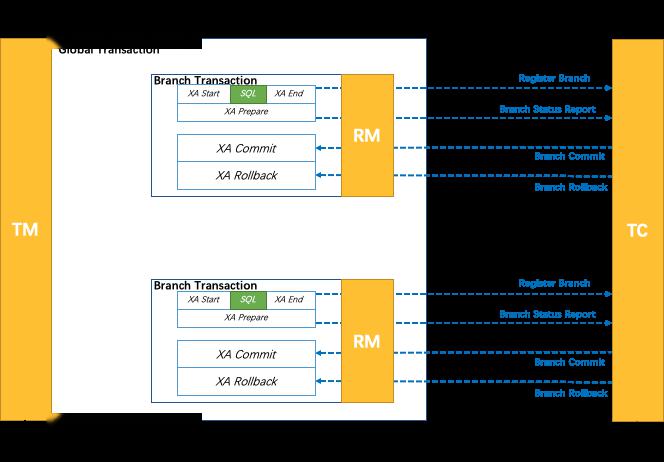
三、核心组件
- TC
维护全局和分支事务的状态,驱动全局事务提交或回滚。
事务协调者
- TM
定义全局事务的范围:开始全局事务、提交或回滚全局事务。
事务发起者。定义事务边界
- RM
管理分支事务处理的资源,与TC交谈以注册分支事务和报告分支事务的状态,并驱动分支事务提交或回滚。
事务参与者
四、为什么需要seata?
首先我们要明白一个点,分布式事务的两阶段提交实现的是数据强一致的模型(SAGA模式除外,SAGA更类似一种业务的补偿方案),必然会对整体的性能造成影响。因此在使用场景上一般是面向营收的业务,另外即便是营收业务,能通过异步解耦实现最终一致性的业务优先选择使用最终一致性。
我们假设下面的一个业务场景。业务A需要支持扣费和优惠券的方式进行支付,我们应该如何实现?
PS:需要20 coin,一张券抵扣10coin,用户钱包需要扣除10coin
1.plan A
产品策略上做修改。先把券兑换成币,然后用币进行消费。如果扣费失败,则券会以币的形式保存在系统中。这种做法本质上绕开了分布式事务的问题。
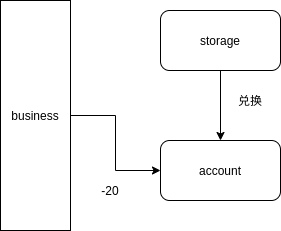
2.plan B
业务发起者维护每个订单的状态,一旦有一个请求超时/失败,则统一调用一个rollback方法回滚每个子事务。
.png)
3.plan C
由于业务需要维护每个子事务的状态,如果有很多业务需要用到这个模型,我们能不能把子事务的状态抽象出来?
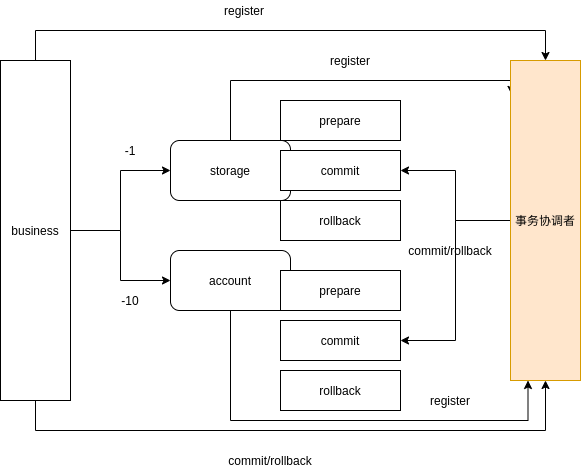
其实这个就是TCC的模式。
4.plan D
我们再继续想想,对于一般的事务而言,其实commit的操作是不用处理任何事情,rollback操作是对prepare操作的反向操作(补偿)。
我们能够通过一个类似binlog的机制,记录下prepare的操作行为,然后根据这个日志自行生成回滚操作?
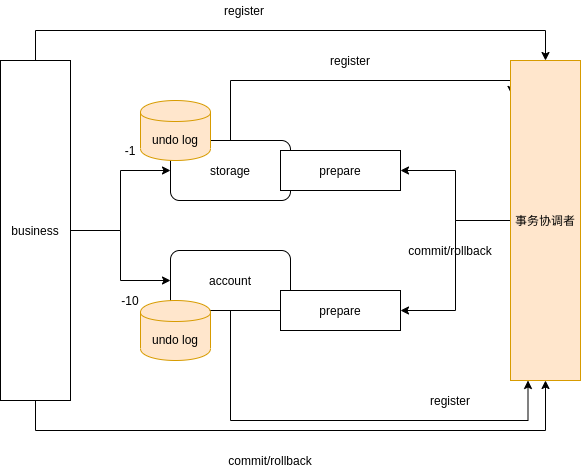
这个就是seata的AT模式
五、源码分析
注:本文使用的版本为v1.2.0
1. undo_log的产生和删除机制
.png)
- undo_log的写入流程
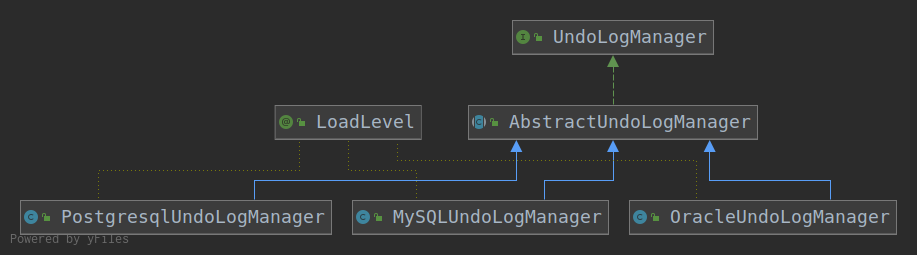
查看flushUndoLogs调用栈
flushUndoLogs:200, AbstractUndoLogManager (io.seata.rm.datasource.undo)
processGlobalTransactionCommit:221, ConnectionProxy (io.seata.rm.datasource)
doCommit:196, ConnectionProxy (io.seata.rm.datasource)
lambda$commit$0:184, ConnectionProxy (io.seata.rm.datasource)
call:-1, 362578118 (io.seata.rm.datasource.ConnectionProxy$$Lambda$197)
execute:289, ConnectionProxy$LockRetryPolicy (io.seata.rm.datasource)
commit:183, ConnectionProxy (io.seata.rm.datasource)
...
execute:108, ExecuteTemplate (io.seata.rm.datasource.exec)
execute:49, ExecuteTemplate (io.seata.rm.datasource.exec)
executeUpdate:64, PreparedStatementProxy (io.seata.rm.datasource)
lambda$update$0:867, JdbcTemplate (org.springframework.jdbc.core)
doInPreparedStatement:-1, 429023383 (org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate$$Lambda$188)
...
//jdbcTemplate执行sql
update:927, JdbcTemplate (org.springframework.jdbc.core)
deduct:51, StorageServiceImpl (io.seata.samples.dubbo.service.impl)
ConnectionProxy为Connection的代理类。
在事务提交之前,做两件事情
- 注册分支事务到TC
- 写入undo_log
private void processGlobalTransactionCommit() throws SQLException {
try {
//**新特性,分支事务注册到TC改为在提交前进行,而不是在一开始就获取一个branchId
register();
} catch (TransactionException e) {
recognizeLockKeyConflictException(e, context.buildLockKeys());
}
try {
//根据数据库的类型获取对应的UndoLogManager进行刷写undolog日志
UndoLogManagerFactory.getUndoLogManager(this.getDbType()).flushUndoLogs(this);
//原connection的commit操作
targetConnection.commit();
} catch (Throwable ex) {
LOGGER.error("process connectionProxy commit error: {}", ex.getMessage(), ex);
report(false);
throw new SQLException(ex);
}
if (IS_REPORT_SUCCESS_ENABLE) {
report(true);
}
context.reset();
}
AbstractUndoLogManager.java
@Override
public void flushUndoLogs(ConnectionProxy cp) throws SQLException {
//通过连接代理获取连接的上下文,这里先不分析xid的传递机制,留给后面的部分进行分析
ConnectionConteConnectionProxyxt connectionContext = cp.getContext();
if (!connectionContext.hasUndoLog()) {
return;
}
String xid = connectionContext.getXid();
long branchId = connectionContext.getBranchId();
BranchUndoLog branchUndoLog = new BranchUndoLog();
branchUndoLog.setXid(xid);
branchUndoLog.setBranchId(branchId);
//具体的undolog的内容
branchUndoLog.setSqlUndoLogs(connectionContext.getUndoItems());
UndoLogParser parser = UndoLogParserFactory.getInstance();
byte[] undoLogContent = parser.encode(branchUndoLog);
if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOGGER.debug("Flushing UNDO LOG: {}", new String(undoLogContent, Constants.DEFAULT_CHARSET));
}
//实际的写入操作,不同的关系型数据库有不同的实现
insertUndoLogWithNormal(xid, branchId, buildContext(parser.getName()), undoLogContent,
cp.getTargetConnection());
}
为了直观显示,我这里给出了一条undo_log的数据
id: 32
branch_id: 2011290555
xid: 172.17.0.1:8091:2011290554
context: serializer=jackson
rollback_info: {"@class":"io.seata.rm.datasource.undo.BranchUndoLog","xid":"172.17.0.1:8091:2011290554","branchId":2011290555,"sqlUndoLogs":["java.util.ArrayList",[{"@class":"io.seata.rm.datasource.undo.SQLUndoLog","sqlType":"UPDATE","tableName":"storage_tbl","beforeImage":{"@class":"io.seata.rm.datasource.sql.struct.TableRecords","tableName":"storage_tbl","rows":["java.util.ArrayList",[{"@class":"io.seata.rm.datasource.sql.struct.Row","fields":["java.util.ArrayList",[{"@class":"io.seata.rm.datasource.sql.struct.Field","name":"id","keyType":"PRIMARY_KEY","type":4,"value":4},{"@class":"io.seata.rm.datasource.sql.struct.Field","name":"count","keyType":"NULL","type":4,"value":201}]]}]]},"afterImage":{"@class":"io.seata.rm.datasource.sql.struct.TableRecords","tableName":"storage_tbl","rows":["java.util.ArrayList",[{"@class":"io.seata.rm.datasource.sql.struct.Row","fields":["java.util.ArrayList",[{"@class":"io.seata.rm.datasource.sql.struct.Field","name":"id","keyType":"PRIMARY_KEY","type":4,"value":4},{"@class":"io.seata.rm.datasource.sql.struct.Field","name":"count","keyType":"NULL","type":4,"value":199}]]}]]}}]]}
log_status: 0
log_created: 2020-05-10 10:02:53
log_modified: 2020-05-10 10:02:53
ext: NULLstruct
这个操作为把用户的库存记录-2。beforeImage的count为201,afterImage的count为199。
- undo_log的生成
ExecuteTemplate.execute
public static <T, S extends Statement> T execute(List<SQLRecognizer> sqlRecognizers,
StatementProxy<S> statementProxy,
StatementCallback<T, S> statementCallback,
Object... args) throws SQLException {
...
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(sqlRecognizers)) {
executor = new PlainExecutor<>(statementProxy, statementCallback);
} else {
if (sqlRecognizers.size() == 1) {
//sqlRecognizer保存了原始的sql执行信息
SQLRecognizer sqlRecognizer = sqlRecognizers.get(0);
//根据不同的SQL类型选择不同的Executor,其主要区别在于beforeImage和afterImage的生成
switch (sqlRecognizer.getSQLType()) {
case INSERT:
executor = new InsertExecutor<>(statementProxy, statementCallback, sqlRecognizer);
break;
case UPDATE:
//UpdateExecutor有一个select for update的逻辑来保证beforeImage&afterImage的准确性,我个人理解local lock指的就是这个地方
executor = new UpdateExecutor<>(statementProxy, statementCallback, sqlRecognizer);
break;
case DELETE:
executor = new DeleteExecutor<>(statementProxy, statementCallback, sqlRecognizer);
break;
case SELECT_FOR_UPDATE:
executor = new SelectForUpdateExecutor<>(statementProxy, statementCallback, sqlRecognizer);
break;
default:
executor = new PlainExecutor<>(statementProxy, statementCallback);
break;
}
} else {
executor = new MultiExecutor<>(statementProxy, statementCallback, sqlRecognizers);
}
}
T rs;
try {
//executor执行
rs = executor.execute(args);
} catch (Throwable ex) {
if (!(ex instanceof SQLException)) {
// Turn other exception into SQLException
ex = new SQLException(ex);
}
throw (SQLException) ex;
}
return rs;
}
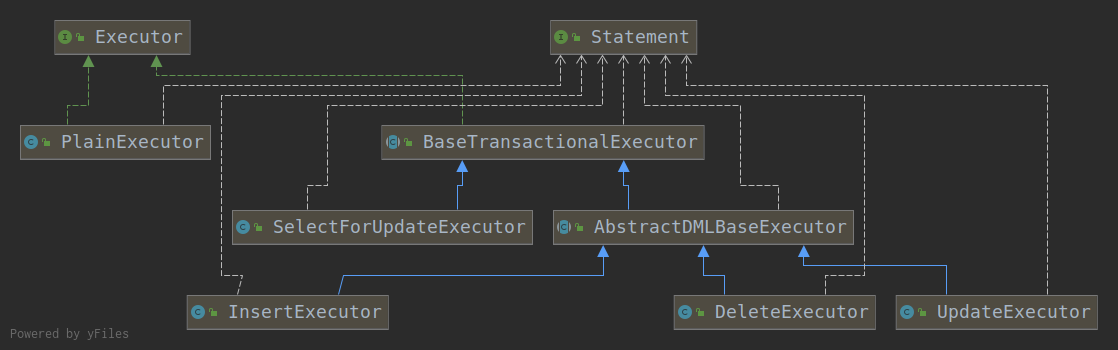
InsertExecutor、UpdateExecutor、DeleteExecutor负责不同的SQL操作生成对应的beforeImage和afterImage。
接下来我们看下rs = executor.execute(args);的执行逻辑
AbstractDMLBaseExecutor.executeAutoCommitFalse
protected T executeAutoCommitFalse(Object[] args) throws Exception {
//生成before image,如果是update和delete操作会有一个select for update的悲观锁
TableRecords beforeImage = beforeImage();
//执行SQL
T result = statementCallback.execute(statementProxy.getTargetStatement(), args);
//获取更新后的afterImage
TableRecords afterImage = afterImage(beforeImage);
//生成undo_log
prepareUndoLog(beforeImage, afterImage);
return result;
}
2.RPC框架整合(xid传递)
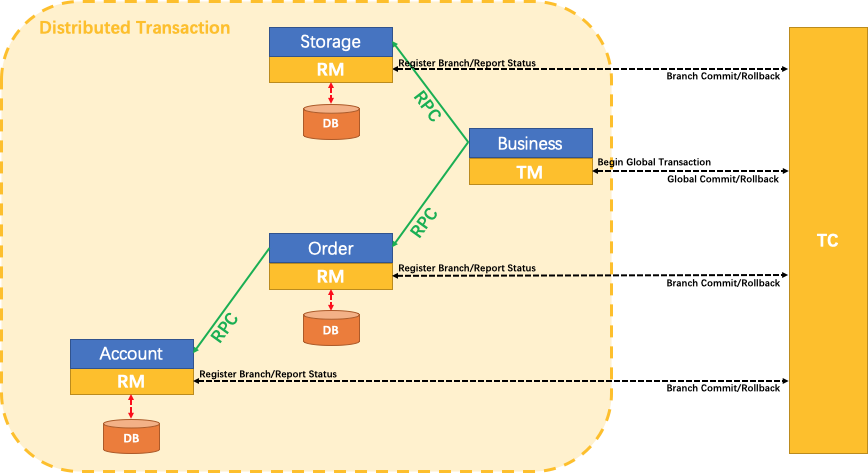
这里的调用关系图忽略了一个细节,所有事务的参与者(TM和RM)都必须通过xid关联起来。那么xid在seata内部又是如何传递的?
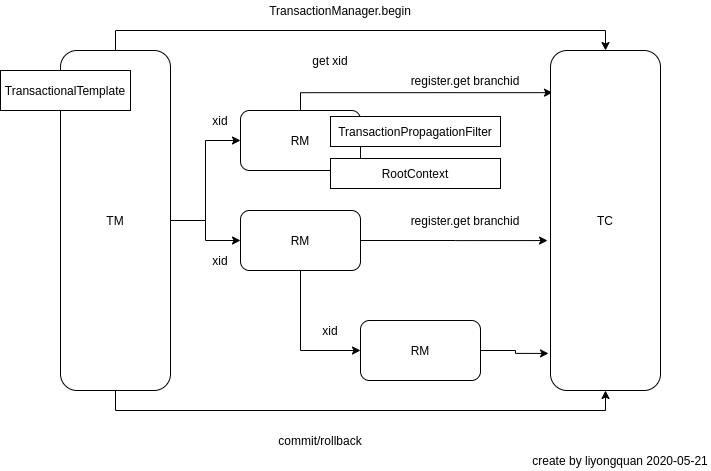
我们从RootContext入手,看下是如何获得xid
/**
* Bind.
*
* @param xid the xid
*/
public static void bind(String xid) {
if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOGGER.debug("bind {}", xid);
}
CONTEXT_HOLDER.put(KEY_XID, xid);
}
/**
* Unbind string.
*
* @return the string
*/
public static String unbind() {
String xid = CONTEXT_HOLDER.remove(KEY_XID);
if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOGGER.debug("unbind {} ", xid);
}
return xid;
}
CONTEXT_HOLDER是一个ThreadLocal的对象。我们来看看RootContext.bind的调用栈
bind:87, RootContext (io.seata.core.context)
begin:106, DefaultGlobalTransaction (io.seata.tm.api)
beginTransaction:175, TransactionalTemplate (io.seata.tm.api)
execute:98, TransactionalTemplate (io.seata.tm.api)
handleGlobalTransaction:106, GlobalTransactionalInterceptor (io.seata.spring.annotation)
invoke:83, GlobalTransactionalInterceptor (io.seata.spring.annotation)
proceed:186, ReflectiveMethodInvocation (org.springframework.aop.framework)
intercept:688, CglibAopProxy$DynamicAdvisedInterceptor (org.springframework.aop.framework)
purchase:-1, BusinessServiceImpl$$EnhancerBySpringCGLIB$$78be133f (io.seata.samples.dubbo.service.impl)
purchase_normal:36, BusinessServiceTest (io.seata.samples.dubbo.service)
核心逻辑在TransactionalTemplate.execute
try {
//RootContext初始化就在这里进行
// 2. begin transaction
beginTransaction(txInfo, tx);
Object rs = null;
try {
// Do Your Business
rs = business.execute();
} catch (Throwable ex) {
// 这里可以看出来回滚是依赖业务逻辑抛出异常触发的
// 3.the needed business exception to rollback.
completeTransactionAfterThrowing(txInfo, tx, ex);
throw ex;
}
// 4. everything is fine, commit.
commitTransaction(tx);
return rs;
} finally {
//5. clear
triggerAfterCompletion();
cleanUp();
}
这里可以比较清晰得看到整个TM/RM的执行流程。
最后在DefaultGlobalTransaction这里类里面初始化RootContext。
public void begin(int timeout, String name) throws TransactionException {
if (role != GlobalTransactionRole.Launcher) {
assertXIDNotNull();
if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOGGER.debug("Ignore Begin(): just involved in global transaction [{}]", xid);
}
return;
}
assertXIDNull();
if (RootContext.getXID() != null) {
throw new IllegalStateException();
}
//请求TC获得xid,这里会通过transactionServiceGroup获取TC的分组的地址(TC资源隔离),获得对应的xid
xid = transactionManager.begin(null, null, name, timeout);
status = GlobalStatus.Begin;
//绑定xid到RootContext
RootContext.bind(xid);
if (LOGGER.isInfoEnabled()) {
LOGGER.info("Begin new global transaction [{}]", xid);
}
}
对于TM,xid是直接从TC获取生成。而RM的xid是由TM在RPC调用的时候同步过来的。下面的RM的DEBUG日志。RM是通过增加一个ApacheDubboTransactionPropagationFilter来保证在接收到请求的时候自动把请求头中的xid解析出来并保存到RootContext。
[DEBUG] 2020-05-11 23:48:46,324 method:io.seata.integration.dubbo.ApacheDubboTransactionPropagationFilter.invoke(ApacheDubboTransactionPropagationFilter.java:48)
xid in RootContext[null] xid in RpcContext[172.17.0.1:8091:2011290575]
[DEBUG] 2020-05-11 23:48:46,324 method:io.seata.core.context.RootContext.bind(RootContext.java:85)
bind 172.17.0.1:8091:2011290575
ApacheDubboTransactionPropagationFilter.invoke
@Override
public Result invoke(Invoker<?> invoker, Invocation invocation) throws RpcException {
String xid = RootContext.getXID();
String xidInterceptorType = RootContext.getXIDInterceptorType();
String rpcXid = getRpcXid();
String rpcXidInterceptorType = RpcContext.getContext().getAttachment(RootContext.KEY_XID_INTERCEPTOR_TYPE);
if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOGGER.debug("xid in RootContext[{}] xid in RpcContext[{}]", xid, rpcXid);
}
boolean bind = false;
if (xid != null) {
RpcContext.getContext().setAttachment(RootContext.KEY_XID, xid);
RpcContext.getContext().setAttachment(RootContext.KEY_XID_INTERCEPTOR_TYPE, xidInterceptorType);
} else {
//绑定rpcXid到RootContext
if (rpcXid != null) {
RootContext.bind(rpcXid);
RootContext.bindInterceptorType(rpcXidInterceptorType);
bind = true;
if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOGGER.debug("bind[{}] interceptorType[{}] to RootContext", rpcXid, rpcXidInterceptorType);
}
}
}
try {
//处理实际的业务逻辑
return invoker.invoke(invocation);
} finally {
//处理请求完成后解绑
if (bind) {
String unbindInterceptorType = RootContext.unbindInterceptorType();
String unbindXid = RootContext.unbind();
...
}
}
}
/**
* get rpc xid
* @return
*/
private String getRpcXid() {
String rpcXid = RpcContext.getContext().getAttachment(RootContext.KEY_XID);
if (rpcXid == null) {
rpcXid = RpcContext.getContext().getAttachment(RootContext.KEY_XID.toLowerCase());
}
return rpcXid;
}
3. 锁的机制(全局锁和局部锁)
Q:两阶段提交的最大的性能瓶颈在哪里?
- 额外增加了一次RPC?
- 锁?
瓶颈在于第一阶段提交和第二阶段提交之间的锁,会大大降低整个分布式事务的吞吐量。因为在第二阶段提交前必须等待所有的事务参与者的prepare操作完成才能进行下一步操作。
假设有3个事务参与者,每个事务参与者在prepare阶段耗时50ms,那么在第二阶段阶段提交前就需要额外增加锁定100ms,吞吐量下降为原来的1/3。
Q:local lock和global lock的区别?
A:本质上没有太大区别。
???????
local lock 使用的是select for update实现,而global lock的锁是由TC进行分配,他们锁定的对象都是表的具体的某一行数据。
假设RM1更新的是account_tbl表,id=1的数据。
.png)
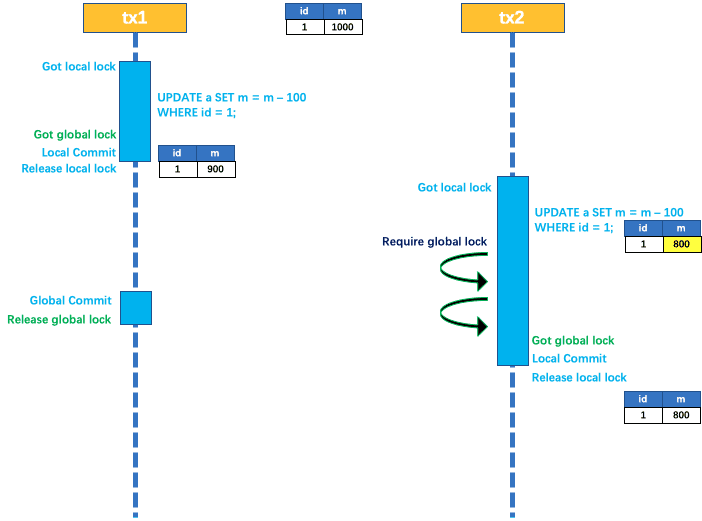
seata的锁分两种local lock和global lock
local lock的核心作用在于保证undo log的准确性。而global lock的主要作用在于保证在全局事务提交之前,RM的数据不会被修改。这里相对第一个版本的优化是在于把global lock放在了第一阶段提交之前进行获取,一定程度上提高了并行度。
 这种事务回滚的方式本质上是触发了死锁导致超时触发的。tx1持有global lock,等待local lock。而tx2持有local lock,等待global lock。最终tx2会超时回滚,从而释放锁,tx1也能继续执行回滚操作。
这种事务回滚的方式本质上是触发了死锁导致超时触发的。tx1持有global lock,等待local lock。而tx2持有local lock,等待global lock。最终tx2会超时回滚,从而释放锁,tx1也能继续执行回滚操作。
- local lock的实现
select for update 实现
- global lock的实现
#RM请求TC获得branchid,并且TC会负责根据lockKey分配锁到TC。
#lockKey的规则为[表名]:[主键ID],多个主键会使用;进行分割
offer message: xid=172.17.0.1:8091:2011468134,branchType=AT,resourceId=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/seata,lockKey=account_tbl:1
在分支事务提交之前,RM会向TC去尝试获得global lock。
ConnectionProxy.processGlobalTransactionCommit
private void processGlobalTransactionCommit() throws SQLException {
try {
//像获取branchid,并且获得global lock
register();
} catch (TransactionException e) {
recognizeLockKeyConflictException(e, context.buildLockKeys());
}
try {
//写入undo_log
UndoLogManagerFactory.getUndoLogManager(this.getDbType()).flushUndoLogs(this);
//事务提交
targetConnection.commit();
} catch (Throwable ex) {
LOGGER.error("process connectionProxy commit error: {}", ex.getMessage(), ex);
report(false);
throw new SQLException(ex);
}
...
}
private void register() throws TransactionException {
if (!context.hasUndoLog() || context.getLockKeysBuffer().isEmpty()) {
return;
}
//注册分支事务
Long branchId = DefaultResourceManager.get().branchRegister(BranchType.AT, getDataSourceProxy().getResourceId(),
null, context.getXid(), null, context.buildLockKeys());
context.setBranchId(branchId);
}
Q:从官方文档我们直观理解global lock是每个RM都锁都是同一把锁,这样才是一个全局的概念。然而在实现过程中同一个xid下的事务的使用的global lock是不一样的。
我尝试写了两个不同的BusinessService,让他们按先后不同的顺序进行扣减操作,然后让他们并发执行。
public class BusinessLockServiceImpl1 implements BusinessLockService1 {
private StorageService storageService;
private AccountService accountService;
@Override
@GlobalTransactional(timeoutMills = 300000, name = "dubbo-demo-tx")
public void purchase(String userId, String commodityCode, int orderCount) {
storageService.deduct(commodityCode, orderCount);
// 计算订单金额
int orderMoney = calculate(commodityCode, orderCount);
accountService.debit(userId,orderMoney);
}
...
}
public class BusinessLockServiceImpl2 implements BusinessLockService2 {
private StorageService storageService;
private AccountService accountService;
@Override
@GlobalTransactional(timeoutMills = 300000, name = "dubbo-demo-tx")
public void purchase(String userId, String commodityCode, int orderCount) {
// 计算订单金额
int orderMoney = calculate(commodityCode, orderCount);
accountService.debit(userId,orderMoney);
storageService.deduct(commodityCode, orderCount);
}
...
}
最终会触发死锁,从而证明我们前面猜想的正确性。
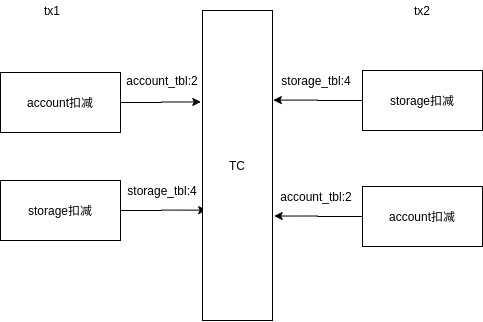
#lockKey=account_tbl:2被xid=2011475475占用
2020-05-13 00:02:19,989 INFO Global lock on [account_tbl:2] is holding by 2011475475
2020-05-13 00:02:19,990 ERROR Catch TransactionException while do RPC, request: xid=172.17.0.1:8091:2011475476,branchType=AT,resourceId=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/seata,lockKey=account_tbl:2
#lockKey=storage_tbl:4被xid=2011475476占用
2020-05-13 00:02:20,182 INFO Global lock on [storage_tbl:4] is holding by 2011475476
2020-05-13 00:02:20,183 ERROR Catch TransactionException while do RPC, request: xid=172.17.0.1:8091:2011475475,branchType=AT,resourceId=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/seata,lockKey=storage_tbl:4
优化方案:
全局锁能否改为由TM发起。TM汇总各RM的资源信息,统一申请一个全局锁?
.png)
个人认为seata的AT模式和XA的模式本质上并没有太大的区别,只是一个由数据库底层支持,一个由应用层实现。为了保证回滚能够正常执行,在第一阶段提交和第二阶段提交之间必须对RM的资源进行加锁,这样都会导致系统的吞吐量急剧下降,有一种说法会降低为原来的1/10。
4.TC-session状态存储
//TODO
目前支持文件和DB进行存储
5.xid生成
//TODO
6.TCC模式
启动DubboTccProviderStarter和DubboTccTransactionStarter
DubboTccProviderStarter–服务提供(事务参与者)
DubboTccTransactionStarter–TCC事务发起者(TM)
AT和TCC模式在设计上最大的区别有以下几点:
- TCC的RM不需要对connection实现代理类(不需要写入undo_log和生成rollback等行为),所以RM的实现及其简单
- 在TM的实现上两者并没有区别,都是TransactionalTemplate来负责通知TC进行commit和rollback的动作
- 没有全局锁和局部锁!!!由于TCC业务侧本身需要保证几个特性(幂等、空回滚、悬挂),本质上相当于回滚的正确性由事务的参与者来保证。(根据base理论,往往可以设置一个处理中的中间态,来避免加锁,实现最终一致性)
7.XA模式
seata-sample的seata-xa子项目
分别启动AccountXAApplicatsion、StorageXAApplication、OrderXAApplication、BusinessXAApplication
#请求BusinessXAApplication
curl 127.0.0.1:8084/purchase
mysql> select * from account_tbl;
+----+---------+-------+
| id | user_id | money |
+----+---------+-------+
| 1 | U100000 | 7000 |
+----+---------+-------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql>
mysql>
mysql>
mysql> select * from order_tbl;
+----+---------+----------------+-------+-------+
| id | user_id | commodity_code | count | money |
+----+---------+----------------+-------+-------+
| 1 | U100000 | C100000 | 30 | 3000 |
+----+---------+----------------+-------+-------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql>
mysql>
mysql>
mysql> select * from storage_tbl;
+----+----------------+-------+
| id | commodity_code | count |
+----+----------------+-------+
| 1 | C100000 | 70 |
+----+----------------+-------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
- TM
TM的逻辑跟TCC和AT的模式是一样的,都统一使用TransactionalTemplate,一旦在RPC调用过程中抛出异常,统一通知TC进行回滚。
- RM
DataSourceProxyXA–XA的数据源连接
PreparedStatementProxyXA
ConnectionProxyXA–XA连接代理
核心的代码在ConnectionProxyXA,本质上结合TC把XA的规范实现一遍。

//xaResource为原始的数据库连接,如果是使用mysql,这里为MysqlXAConnection
/**
* XA commit
* @param xid global transaction xid
* @param branchId transaction branch id
* @throws SQLException
*/
public void xaCommit(String xid, long branchId, String applicationData) throws XAException {
XAXid xaXid = XAXidBuilder.build(xid, branchId);
xaResource.commit(xaXid, false);
releaseIfNecessary();
}
/**
* XA rollback
* @param xid global transaction xid
* @param branchId transaction branch id
* @throws SQLException
*/
public void xaRollback(String xid, long branchId, String applicationData) throws XAException {
XAXid xaXid = XAXidBuilder.build(xid, branchId);
xaResource.rollback(xaXid);
releaseIfNecessary();
}
//xa start
@Override
public void setAutoCommit(boolean autoCommit) throws SQLException {
if (currentAutoCommitStatus == autoCommit) {
return;
}
if (autoCommit) {
// According to JDBC spec:
// If this method is called during a transaction and the
// auto-commit mode is changed, the transaction is committed.
if (xaActive) {
commit();
}
} else {
if (xaActive) {
throw new SQLException("should NEVER happen: setAutoCommit from true to false while xa branch is active");
}
// Start a XA branch
long branchId = 0L;
try {
// 1. register branch to TC then get the branchId
//请求TC获得branchId
branchId = DefaultResourceManager.get().branchRegister(BranchType.XA, resource.getResourceId(), null, xid, null,
null);
} catch (TransactionException te) {
...
}
// 2. build XA-Xid with xid and branchId
this.xaBranchXid = XAXidBuilder.build(xid, branchId);
try {
// 3. XA Start
xaResource.start(this.xaBranchXid, XAResource.TMNOFLAGS);
} catch (XAException e) {
...
}
// 4. XA is active
this.xaActive = true;
}
currentAutoCommitStatus = autoCommit;
}
@Override
public void commit() throws SQLException {
...
try {
// XA End: Success
xaResource.end(xaBranchXid, XAResource.TMSUCCESS);
// XA Prepare
xaResource.prepare(xaBranchXid);
// Keep the Connection if necessary
keepIfNecessary();
} catch (XAException xe) {
...
} finally {
cleanXABranchContext();
}
}
8.HA
主要分析TC的高可用
