前言
上一篇分析到NioEventLoopGroup会构建一系列的NioEventLoop线程。那么NioEventLoop线程到底是做了什么事情?
children = new EventExecutor[nThreads];
for (int i = 0; i < nThreads; i ++) {
boolean success = false;
try {
children[i] = newChild(executor, args);
success = true;
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: Think about if this is a good exception type
throw new IllegalStateException("failed to create a child event loop", e);
} finally {
...
}
}
创建NioEventLoop
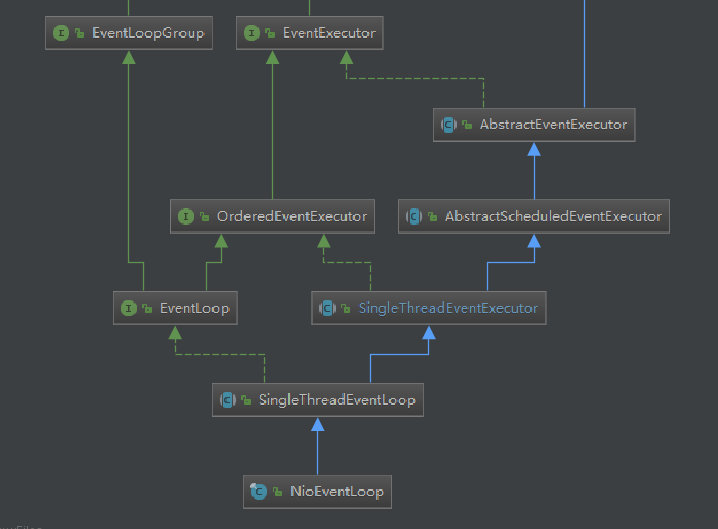
我们先看下NioEventLoop的类图
NioEventLoop(NioEventLoopGroup parent, Executor executor, SelectorProvider selectorProvider,
SelectStrategy strategy, RejectedExecutionHandler rejectedExecutionHandler,
EventLoopTaskQueueFactory queueFactory) {
super(parent, executor, false, newTaskQueue(queueFactory), newTaskQueue(queueFactory),
rejectedExecutionHandler);
if (selectorProvider == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("selectorProvider");
}
if (strategy == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("selectStrategy");
}
provider = selectorProvider;
final SelectorTuple selectorTuple = openSelector();
selector = selectorTuple.selector;
unwrappedSelector = selectorTuple.unwrappedSelector;
selectStrategy = strategy;
}
- taskQueue初始化
private static Queue<Runnable> newTaskQueue0(int maxPendingTasks) {
// This event loop never calls takeTask()
return maxPendingTasks == Integer.MAX_VALUE ? PlatformDependent.<Runnable>newMpscQueue()
: PlatformDependent.<Runnable>newMpscQueue(maxPendingTasks);
}
初始化一个MpscQueue(Multi producer single consumer)作为NioEventLoop的内存队列使用,这个队列是JCTool提供的一个实现无锁的高并发队列。这里暂时不对其进行过多的分析,我们只需要知道我们初始化了这个队列即可。
- openSelector。打开一个NIO的选择器。
final Selector unwrappedSelector;
try {
unwrappedSelector = provider.openSelector();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new ChannelException("failed to open a new selector", e);
}
if (DISABLE_KEY_SET_OPTIMIZATION) {
return new SelectorTuple(unwrappedSelector);
}
如果关闭了key-set优化,默认是使用java nio的selector。具体的优化逻辑这里先不进行讨论。
接下来我们尝试分析下taskQueue和selector具体在哪个地方使用。
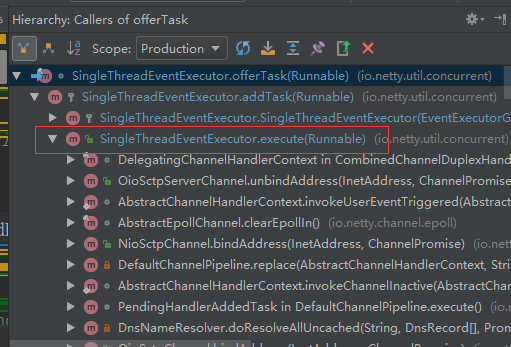
TaskQueue的使用
写TaskQueue队列。SingleThreadEventExecutor.offerTask
@Override
public void execute(Runnable task) {
logger.info("SingleThreadEventExecutor execute...task:{}",task);
if (task == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("task");
}
//判断当前线程是否EventLoop的线程,作用是?
boolean inEventLoop = inEventLoop();
//添加任务
addTask(task);
if (!inEventLoop) {
startThread();
if (isShutdown()) {
...
}
}
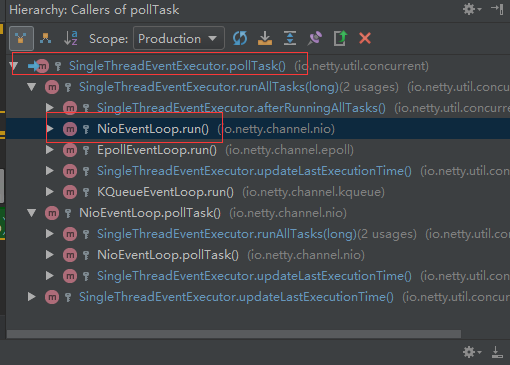
TaskQueue的出队。
总结
本次先对NioEventLoop有个大致地了解,后面再深入对里面的细节进行分析。
