一、开篇
hystix相信大家都不陌生。github地址:https://github.com/Netflix/Hystrix。中文名称翻译为刺猬,顾明思议是用来保护我们系统的。在分布式系统中可能会依赖很多服务,当依赖的服务出现异常,接口时延上涨,超时,很有可能会把上游业务的接口给拖死,把线程资源耗尽。我们需要一种机制对依赖服务的可用性做分析,如果依赖服务的失败率异常,能够做到类似保险丝的作用,把流量切断,避免产生更严重的故障。 其中最核心的组建就是里面的断路器。我们主要分析两点:
- 何时决定把断路器打开
- 当依赖服务恢复的时候如何自动恢复
二、源码分析
1. 整体流程
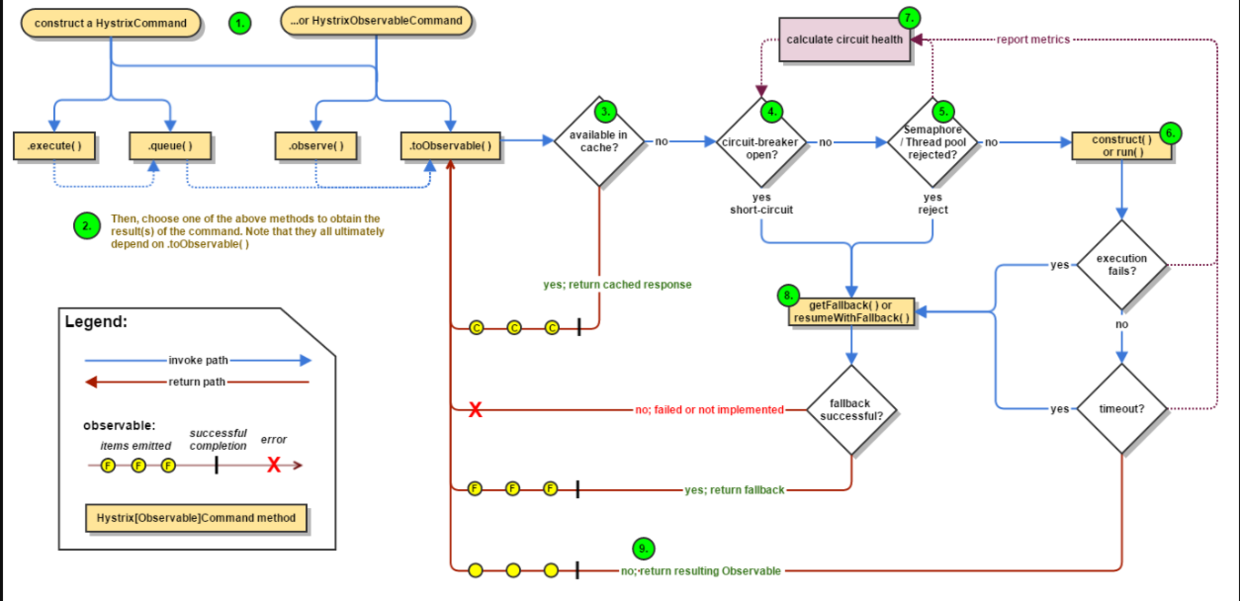
我们借用hystrix wiki上的一张图来简单了解整个流程。本次关注的核心点是4,7。也就是断路器的实现逻辑。
2. 断路器实现
断路器的接口:HystrixCircuitBreaker
/**
* Circuit-breaker logic that is hooked into {@link HystrixCommand} execution and will stop allowing executions if failures have gone past the defined threshold.
* <p>
* The default (and only) implementation will then allow a single retry after a defined sleepWindow until the execution
* succeeds at which point it will again close the circuit and allow executions again.
*/
public interface HystrixCircuitBreaker {
/**
* Every {@link HystrixCommand} requests asks this if it is allowed to proceed or not. It is idempotent and does
* not modify any internal state, and takes into account the half-open logic which allows some requests through
* after the circuit has been opened
*
* @return boolean whether a request should be permitted
*/
boolean allowRequest();
/**
* Whether the circuit is currently open (tripped).
*
* @return boolean state of circuit breaker
*/
boolean isOpen();
/**
* Invoked on successful executions from {@link HystrixCommand} as part of feedback mechanism when in a half-open state.
*/
void markSuccess();
/**
* Invoked on unsuccessful executions from {@link HystrixCommand} as part of feedback mechanism when in a half-open state.
*/
void markNonSuccess();
/**
* Invoked at start of command execution to attempt an execution. This is non-idempotent - it may modify internal
* state.
*/
boolean attemptExecution();
我们重点关注两个方法allowRequest和isOpen,分别是判断是否允许流量进来和断路器开启关闭的核心接口。 HystrixCircuitBreaker有两个实现类。分别是:
- NoOpCircuitBreaker 空实现类
- HystrixCircuitBreakerImpl
默认实现类。本次分析的重点就是这个类。
3. 调用栈
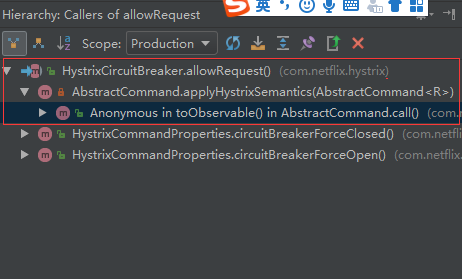
我们重点看下applyHystrixSemantics这个方法。
private Observable<R> applyHystrixSemantics(final AbstractCommand<R> _cmd) {
// mark that we're starting execution on the ExecutionHook
// if this hook throws an exception, then a fast-fail occurs with no fallback. No state is left inconsistent
executionHook.onStart(_cmd);
/* determine if we're allowed to execute */
if (circuitBreaker.allowRequest()) {
...
} else {
return handleShortCircuitViaFallback();
}
}
通过断路器控制是否应该走正常的调用逻辑。
4. 断路器判断逻辑
@Override
public boolean allowRequest() {
if (properties.circuitBreakerForceOpen().get()) {
// properties have asked us to force the circuit open so we will allow NO requests
return false;
}
if (properties.circuitBreakerForceClosed().get()) {
// we still want to allow isOpen() to perform it's calculations so we simulate normal behavior
isOpen();
// properties have asked us to ignore errors so we will ignore the results of isOpen and just allow all traffic through
return true;
}
return !isOpen() || allowSingleTest();
}
- 若断路器关闭,则允许访问。
- 否则尝试放行一部分流量进来验收依赖服务是否正常
接下来看isOpen的实现方法。
@Override
public boolean isOpen() {
if (circuitOpen.get()) {
// if we're open we immediately return true and don't bother attempting to 'close' ourself as that is left to allowSingleTest and a subsequent successful test to close
return true;
}
// we're closed, so let's see if errors have made us so we should trip the circuit open
HealthCounts health = metrics.getHealthCounts();
//请求总数没有达到设置的请求阈值,不会打开断路器。(对于请求太少的场景,失败率没有太大意义)
// check if we are past the statisticalWindowVolumeThreshold
if (health.getTotalRequests() < properties.circuitBreakerRequestVolumeThreshold().get()) {
// we are not past the minimum volume threshold for the statisticalWindow so we'll return false immediately and not calculate anything
return false;
}
//当失败率大于某个阈值的时候,把断路器打开。
if (health.getErrorPercentage() < properties.circuitBreakerErrorThresholdPercentage().get()) {
return false;
} else {
//这里要考虑并发的场景,所以使用CAS的操作
// our failure rate is too high, trip the circuit
if (circuitOpen.compareAndSet(false, true)) {
// if the previousValue was false then we want to set the currentTime
//设置断路器的开启时间是为了让服务在一定的时间范围内接受少量的流量来决定是否需要把断路器重新关闭。
circuitOpenedOrLastTestedTime.set(System.currentTimeMillis());
return true;
} else {
// How could previousValue be true? If another thread was going through this code at the same time a race-condition could have
// caused another thread to set it to true already even though we were in the process of doing the same
// In this case, we know the circuit is open, so let the other thread set the currentTime and report back that the circuit is open
return true;
}
}
}
}
isOpen的逻辑很清晰,简而言之就是当失败率大于某个阈值的时候会把断路器打开。 接下来我们重点看下allowSingleTest的方法。
public boolean allowSingleTest() {
long timeCircuitOpenedOrWasLastTested = circuitOpenedOrLastTestedTime.get();
// 1) if the circuit is open
// 2) and it's been longer than 'sleepWindow' since we opened the circuit
if (circuitOpen.get() && System.currentTimeMillis() > timeCircuitOpenedOrWasLastTested + properties.circuitBreakerSleepWindowInMilliseconds().get()) {
// We push the 'circuitOpenedTime' ahead by 'sleepWindow' since we have allowed one request to try.
// If it succeeds the circuit will be closed, otherwise another singleTest will be allowed at the end of the 'sleepWindow'.
if (circuitOpenedOrLastTestedTime.compareAndSet(timeCircuitOpenedOrWasLastTested, System.currentTimeMillis())) {
// if this returns true that means we set the time so we'll return true to allow the singleTest
// if it returned false it means another thread raced us and allowed the singleTest before we did
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
逻辑很简单,就是在一定的时间窗口内只会放行一个请求。eg. 在23:00 00.000的时间开启了断路器,假设断路器的时间窗口设置为100ms。则在23:00 00.000~23:00 00.100只会允许一个请求通过。 这个主要是为了验证依赖服务是否已经恢复正常。
三、总结
这篇文章主要简单分析了断路器的判断逻辑。接下来会重点分析下断路器的数据收集的逻辑实现(HystrixCommandMetrics)。另外hystirx大量用了命令模式的实现(rxjava),这块逻辑也是里面理解起来比较费力的地方。
